远程调用
2016-02-24 13:46:04
# talk
首先,定义一下本文中的几个概念:
远程调用:跨进程的方法调用
客户进程:发起方法调用的进程
服务进程:实际实现方法的进程
如果需要设计一个“远程调用”的机制,我们需要考虑以下几个问题:
- 客户进程如何发起方法调用
- 服务进程如何知道要调用的方法名,如何接收方法参数
- 客户进程与服务进程如何通信
基础模式如下:
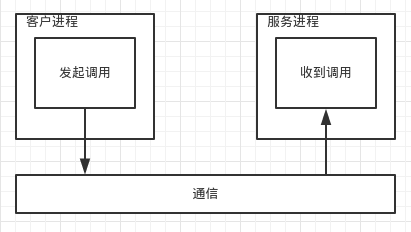
HTTP
如果按照这里的定义,HTTP 访问本质上也是一个远程调用。针对 HTTP 协议规范,我们看看它的实现原理:
用户在浏览器地址栏输入“http://www.chelaile.net.cn/index.html”,然后打开一个网页
浏览器内部发起http请求
即:
GET /index.html HTTP/1.1
Host: www.chelaile.net.cn
代码表示如下:
browser.open("http://www.chelaile.net.cn/index.html");
browser.parse("http://www.chelaile.net.cn/index.html");
data = browser.marshalling({
Host : www.chelaile.net.cn,
method : get,
page : /index.html
});
browser.send(data)
浏览器通过 TCP 协议将 data 发往服务器
服务器接收 data
即:
server.receive(data);
server.unmarshalling(data); //得到{
Host : www.chelaile.net.cn,
method : get,
page : /index.html
}
server.get("/index.html");
所以,远程调用的核心过程就是:
- 客户进程与服务进程协商编组格式,即“协议”
- 客户进程将“调用”本身所需的所有数据按照“协议”进行编组
- 客户进程将编组后的数据发送给服务进程
- 服务进程收到数据之后按照“协议”进行反编组
- 服务进程根据反编组后的数据进行相应的方法调用
通常来说,第3步属于底层通信细节,是“协议”独立的。所以,使用Socket即可。图形表示如下:
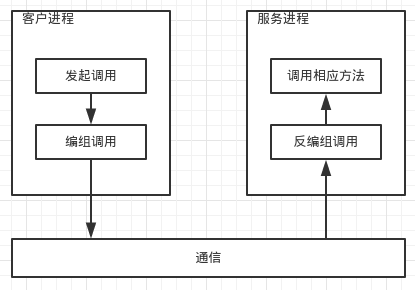
RPC
RPC 的 5 个部分:
- Client
- Client-stub
- RPCRuntime
- Server-stub
- Server
对应表示即:
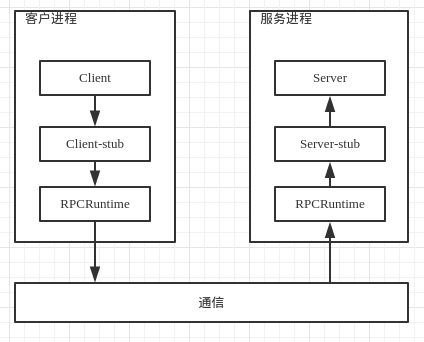
RMI
RPC 更接近于“远程调用”协议,而 RMI 就是特定的 java “远程调用”实现了。由于 java 不能进行动态类或者方法定义,所以一切调用都是基于接口来进行。
一个简单的例子如下:
- 约定服务接口
public interface IHelloService extends Remote {
public String sayHello() throws RemoteException;
}
- 实现服务
public class HelloServiceImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject implements IHelloService {
protected HelloServiceImpl() throws RemoteException {
}
protected HelloServiceImpl(int port) throws RemoteException {
super(port);
}
protected HelloServiceImpl(int port, RMIClientSocketFactory csf, RMIServerSocketFactory ssf) throws RemoteException {
super(port, csf, ssf);
}
@Override
public String sayHello() throws RemoteException {
return "this is ServiceImpl";
}
}
- 注册服务
public class HelloServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
IHelloService service = new HelloServiceImpl();
LocateRegistry.createRegistry(20000);
Naming.bind("rmi://localhost:20000/Hello", service);
} catch (AlreadyBoundException | MalformedURLException | RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("bind success");
}
}
- 客户端查找服务并调用
public class HelloClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
IHelloService helloService = (IHelloService) Naming.lookup("rmi://localhost:20000/Hello");
String resp = helloService.sayHello();
System.out.println(resp);
} catch (NotBoundException | MalformedURLException | RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//output
this is ServiceImpl
上面的代码中并没有具体的“编组”或者 stub 相关的代码,因为 RMI 处理了这些细节,从而在更高的层面来对外提供接口。