其实这是一个面试题。
线程状态
按照 Thread.State 的定义,一个线程可能处在以下六种状态之一 :
NEW
线程对象被创建,但是还未开始。即还没有调用过 Thread.start
RUNNABLE
线程正在运行,或者等待分配运行资源
BLOCKED
等待进入同步块(monitor lock),注意与Lock对象的区别。
或者在调用 Object.wait 之后再次进入同步的块/方法(意思就是再次进入的这个时候依旧没有获取到锁)。
WAITING
等待其他线程的操作,触发进入此状态是操作:
Object.wait with no timeout
Thread.join with no timeout
LockSupport.park //比如condition.await()
TIMED_WAITING
等待一定的时间
Thread.sleep
Object.wait with timeout
Thread.join with timeout
LockSupport.parkNanos
LockSupport.parkUntil
TERMINATED
线程已经执行完成
问题来了,如何按照顺序打印同一个线程的不同状态
比如,要求的顺序是
NEW -> RUNNABLE -> WAITING -> BLOCKED -> TIMED_WAITING -> TERMINATED
一个线程肯定没有办法完全依靠自身来完成所有要求,所以这里需要一个控制线程,来控制“从线程”,让“从线程”处于不同的状态,然后打印“从线程”状态。
大致过程:
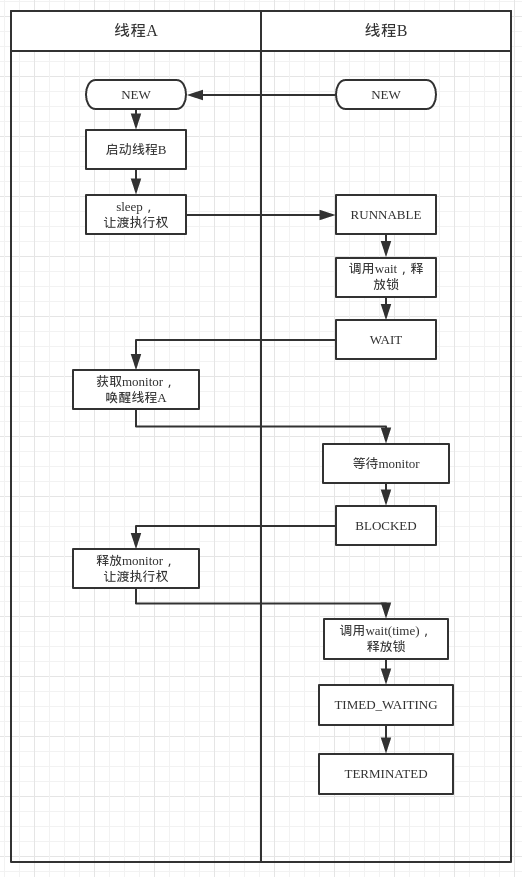
一个不完善的实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
| public class ThreadStatePrinter {
static final Object obj = new Object();
static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
static Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread slaveThread = new Thread("slaveThread") {
@Override
public void run() {
log(2, this);
lock.lock();
try {
condition.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
lock.unlock();
synchronized (obj) {
try {
obj.wait(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
lock.lock();
condition.signalAll();
lock.unlock();
}
};
Thread controlThread = new Thread(() -> {
log(1, slaveThread);
slaveThread.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log(3, slaveThread);
lock.lock();
condition.signalAll();
synchronized (obj) {
lock.unlock();
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log(4, slaveThread);
}
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log(5, slaveThread);
lock.lock();
try {
condition.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
lock.unlock();
log(6, slaveThread);
}, "controlThread");
controlThread.start();
}
public static void log(int index, Thread thread) {
System.out.println(index + ":" + thread.getName() + ":" + thread.getState().toString());
}
}
|
